Published on 14th July 2017
In efforts to reduce iron deficiency in populations, governments are increasingly choosing iron sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (NaFeEDTA) as the form of iron to be added to wheat and maize flour (1). This form of iron is highly bioavailable and more readily absorbed by the body compared to other forms such as electrolytic iron, ferrous sulfate or fumarate; and effective in reducing iron deficiency and related anemia (2).
iCheck Iron measurement of NaFeEDTA in flour sped up
Our users noted that, although easy to use, the long reaction time of the iCheck Iron made it challenging to test flour fortified with iron EDTA. BioAnalyt partnered with AkzoNobel, manufacturer of high quality NaFeEDTA (Ferrazone®), to develop an improved and faster reagent mix for measuring NaFeEDTA with iCheck Iron. Now we offer you iCheck Iron Test Kit with a new Additive that reduces reaction time from 6 hours to only 60 minutes. BioAnalyt and AkzoNobel hope this development will enable effective monitoring of the fortification process to ensure compliance and deliver the intended health impact.
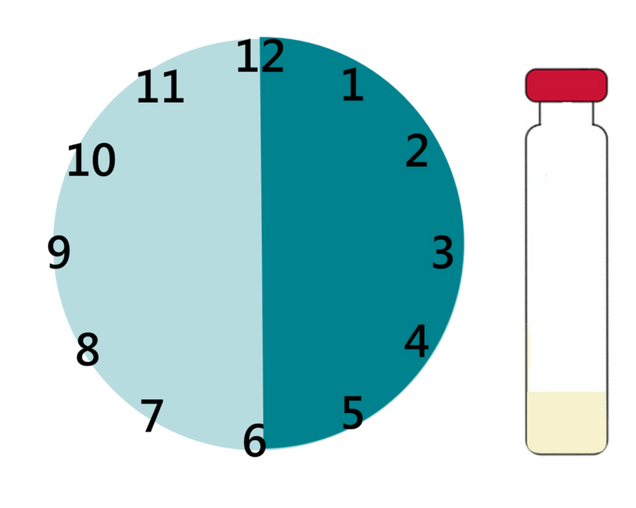
Old Additive
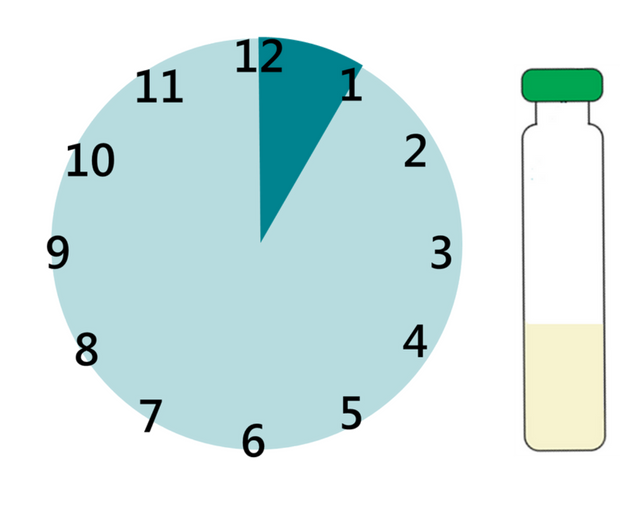
New Additive
Differentiation of iron EDTA from other iron forms
Iron EDTA is a water soluble form of iron. This allows differentiation of iron EDTA from intrinsic iron, iron fumarate or iron sulfate when measuring with iCheck Iron.
Do I need a new iCheck Iron device?
No, it is only the Additive in the iCheck Iron Test Kit that has changed. Since January 2017, all iCheck Iron Test Kits include the new and improved Additive.
References
1. WHO. Nutrition: Recommendations on Wheat and Maize Flour Fortification Meeting Report: Interim Consensus Statement. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland.; 2009.
2. An Evaluation of EDTA Compounds for Iron Fortification of Cereal-Based Foods. RF Hurrell et al. Br J Nutr 84 (6), 903-910. 12 2000.
